Triaging calls effectively can make all the difference between a smooth day and a chaotic one. With each call representing a unique customer need—whether it's a technical issue, a product question, or a complaint—it's crucial to assess and prioritize how to handle them quickly. Without a clear process, customers may experience longer wait times, frustration may build, and your team can quickly feel overwhelmed.
Triage, in simple terms, means sorting and prioritizing calls so that each one gets the attention it needs when it needs it. But there's more to it than just answering the phone. It's about recognizing when a customer is frustrated, ensuring VIP customers don't have to wait, and knowing when to escalate a situation to a supervisor.
In this blog, we'll explore some practical strategies to help you fine-tune your triage process, from spotting emotional cues in customer messages to setting up systems that ensure urgent calls are handled immediately. Whether managing a high volume of calls or trying to create a more personalized customer experience, these tips will help you work smarter, not harder, and improve customer satisfaction.
Understanding Call Triage: What Does it Mean?
Call triage means assessing, prioritizing, and directing incoming customer inquiries to the right department or agent. It ensures that each call is handled promptly and efficiently based on its urgency and complexity, helping to resolve issues quickly and improving overall customer satisfaction.
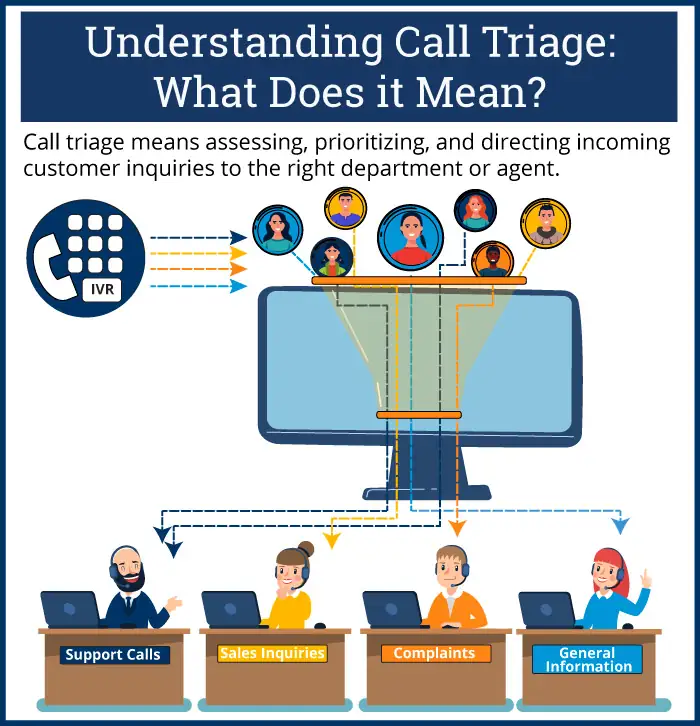
Effective triage begins with clearly understanding the different types of calls in your call center. Calls vary in complexity, urgency, and purpose, and handling each one appropriately is key to providing excellent service.
1. Understanding Call Types
The first step in triage is to identify the nature of the call quickly. Common call types include:
- Support Calls: These are calls where customers need help with a product or service—whether it's technical support, troubleshooting, or assistance with a service issue.
- Sales Inquiries: Customers may call to ask about product details, make a purchase, or inquire about new offerings.
- Complaints: Calls where customers are dissatisfied with the product, service, or experience. These require special attention to prevent escalation.
- General Information Requests: These are basic questions about hours, location, policies, or other general details.
Identifying these call types early helps direct customers to the right team or department faster, reducing unnecessary wait times and preventing frustration.
2. Assessing Urgency and Complexity
Once the call type is identified, the next step is determining its urgency and complexity. Not all calls are created equal, and some need to be handled immediately, while others can wait. For example:
- Urgent Calls: These include issues like service outages, technical failures, or emergencies where the customer is unable to use a product or service. These calls should be fast-tracked to ensure quick resolution.
- Complex Calls: Some calls may be complex but not urgent—like troubleshooting a complicated technical issue. These require knowledgeable staff to assist and may need to be escalated to specialists.
- Routine Calls: Simple inquiries, such as asking about store hours or account details, are less urgent and can be handled by entry-level agents or through automated systems.
By assessing the urgency and complexity of the call early in the process, agents can prioritize the most pressing issues without neglecting other inquiries. This leads to quicker resolutions, better customer satisfaction, and more efficient use of resources.
5 Strategies for Fine-Tuning Your Call Canter's Triage Process

1. Use Sentiment Analysis to Identify Emotional Cues in Conversations
Sentiment analysis tools scan the text for specific keywords or phrases that convey emotion, but it's also important to pay attention to subtle cues. Some key indicators of frustration include negative language, repetitive complaints, and urgency. For example, if a customer says, "This has been going on too long," that signals that the call needs to be handled more urgently.
Additionally, sentiment analysis tools can automate this process, flagging high-risk cases for agents to address sooner. This allows the call center to operate more efficiently, responding to the customer's emotional state and improving both customer satisfaction and agent productivity.
Incorporating sentiment analysis into your triage strategy helps create a more responsive and customer-centric call center where emotional cues are heard and acted upon in a timely and meaningful way.
2. Prioritize VIP Customers for Faster Service
While every customer deserves attention and a timely resolution, certain customers' needs may warrant a faster response. These are your VIP customers—those with long-standing relationships, high-value accounts, or urgent needs that require immediate attention. Fast-tracking VIP customers can significantly impact customer loyalty, satisfaction, and overall business success.
Creating Rules for Fast-Tracking VIP Customers
To efficiently manage VIP customer calls, your call center should implement rules that allow for immediate identification and prioritization. Here are some ways to build a VIP triage system:
- Customer Profiles and CRM Integration: Utilize customer relationship management (CRM) tools to store detailed profiles that identify high-value customers.
- Special Phone Lines or Channels: Set up a dedicated phone line, email address, or chat channel for VIP customers. This ensures that these customers can quickly bypass general queues and reach an agent.
- Queue Prioritization Rules: Establish automated routing rules prioritizing VIP customers in your call queue.
- Alert Systems: When a VIP customer calls, the system must notify the agent immediately, even before the call is answered. Setting up alerts or flags in your call center software can help agents recognize a VIP call.
While it's important to prioritize VIP customers, it's essential to ensure that this doesn't negatively impact the experience of other callers. A well-balanced approach is needed to avoid alienating non-VIP customers. If VIP calls are given too much priority, other customers may feel neglected, leading to dissatisfaction and potential churn.

3. Set Up a Separate Telephone Number for Urgent Calls
In a call center, high-priority customers or urgent issues often require special handling to ensure quick resolution. One effective way to streamline this process is by setting up a dedicated phone number or line for high-priority routing. This ensures that critical cases are addressed without delay and keeps the regular queue running smoothly for other customers.
A dedicated line for high-priority calls serves several purposes:
- Improved Response Times: VIP customers or urgent situations can be immediately identified and routed to agents without waiting in a general queue.
- Minimized Interruption to Regular Flow: Agents can focus on solving urgent issues by isolating high-priority calls from the regular queue. In contrast, other calls continue to be answered at normal speed. This prevents bottlenecks and helps maintain a balance in call center operations.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: For customers with time-sensitive needs, knowing they have a direct, dedicated line to resolve their issue builds trust and reinforces the value they place on their relationship with your company.
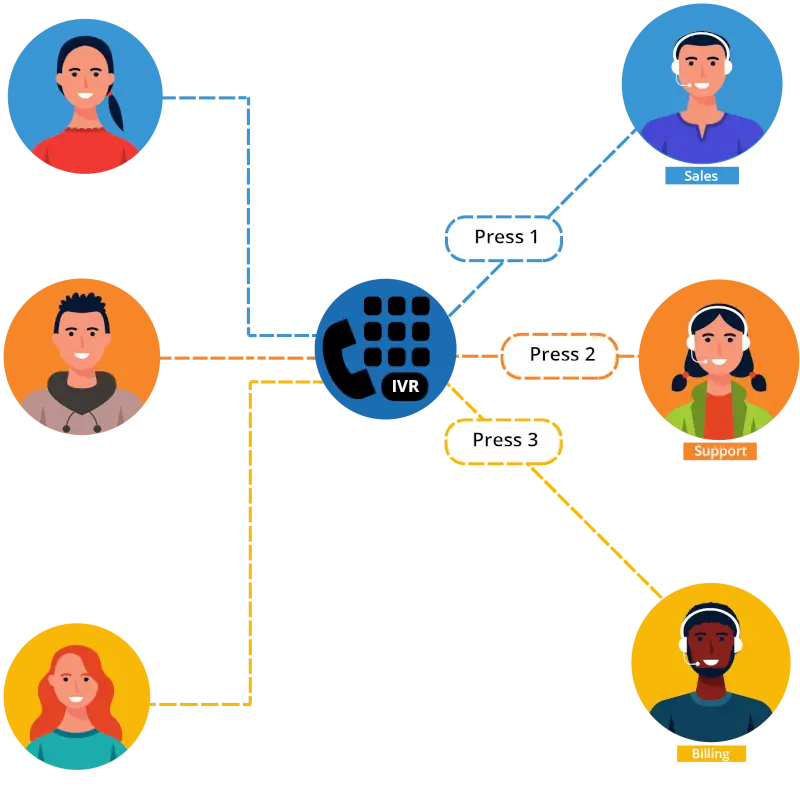
4. Don't Overload Your IVR with Too Many Subcategories
IVR systems are often used to streamline the call center process by directing customers to the right department or information. While IVR systems are invaluable for managing high call volumes, there's a fine line between a helpful, well-organized system and one that frustrates your customers. One of the key pitfalls to avoid is overcomplicating your IVR with too many subcategories, which can actually lengthen wait times and increase customer frustration.
While it may seem intuitive to create multiple subcategories in your IVR to handle specific needs, too many options can have unintended consequences:
- Longer Decision Time: When customers are faced with an overwhelming number of options, they may struggle to select the right one. This frustration can lead to more abandoned calls, longer wait times, and a higher likelihood of customers pressing the wrong option and getting routed to the wrong department.
- Increased Queue Time: Ironically, while subcategorizing is meant to reduce wait times by directing calls more efficiently, too many options can cause the system to route calls into longer queues, resulting in bottlenecks and longer hold times.
- Customer Frustration: If customers feel like they are getting lost in the maze of menu options or don't know how to navigate the IVR system effectively, they are likely to become frustrated and disengage.
One way to avoid these pitfalls is to allow quick access to a live agent. This gives customers an easy way to skip the IVR and speak with an agent directly if they're frustrated or have a complex issue. This ensures that the experience is not overly time-consuming for those who need immediate help.
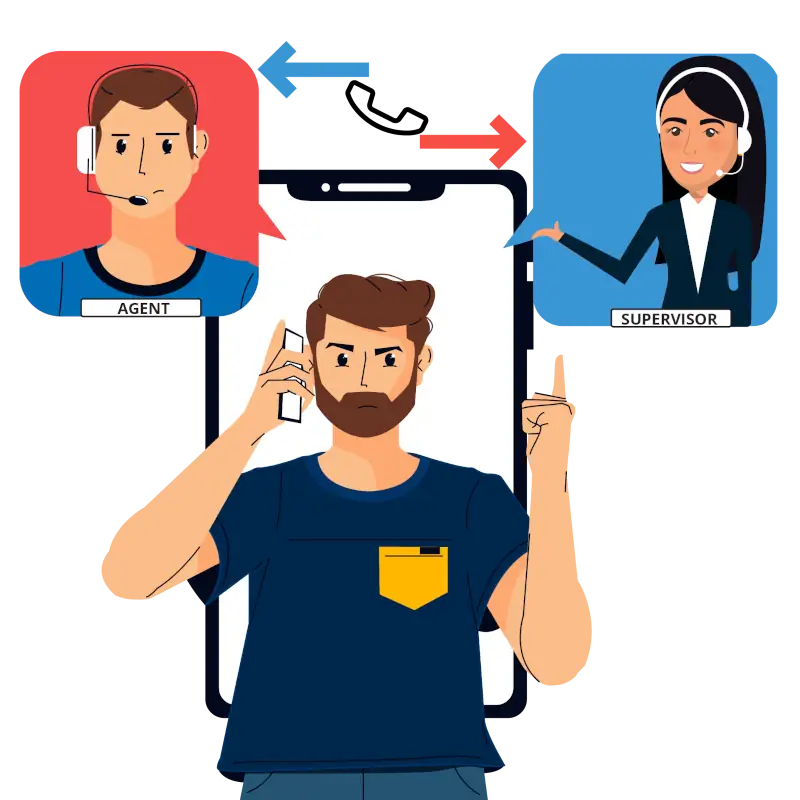
5. Alert Supervisors to Step in and Resolve Urgent Issues
In any call center, there will be situations where an issue is too complex or urgent for the frontline agent to handle alone. These cases require the intervention of a supervisor or manager, and the ability to quickly alert them is a critical part of effective triaging. Knowing when to escalate a call to a higher level is vital to maintaining customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Common scenarios that require supervisor intervention include:
- Escalated Complaints: If a customer is dissatisfied with the solution or service provided, involving a supervisor can help to de-escalate the situation and deliver a more effective resolution.
- Complex Technical Issues: Supervisors may need to step in to resolve technical problems that require expert knowledge or access to advanced tools swiftly.
- Urgent Cases: In cases of critical importance, such as system outages, billing issues, or time-sensitive requests, immediate supervisor action is needed to prevent further disruption.
An effective escalation process ensures that urgent issues are resolved quickly and efficiently while providing agents with the support they need to manage complex or sensitive situations. Supervisors can make all the difference in keeping things running smoothly and ensuring customer satisfaction remains high.
