What Is Customer Feedback?
Customer feedback is the information they provide about their call center interaction experience. It can come from customer feedback methods such as phone, email, online surveys, speech analytics, social media, an agent asking a customer, quality assurance, and operational data.
Call center customer feedback often tells you what you are good at delivering and what needs improvement. Sometimes, it requires multiple customer feedback methods to understand the opportunities to improve customer experience (CX) using a call center so you can translate the information into meaningful action.
Why Is Customer Feedback Important?
Customer feedback is important because it is a pillar for delivering great customer satisfaction. Without an effective customer feedback program, it is unlikely for your call center to provide great customer service and make a strong contribution to helping your company retain customers.
Think of it this way: 95% of customers will continue to do business with a company because they have experienced great customer service interacting with a call center. Conversely, 88% of customers have stopped doing business with a company because of poor call center customer service. But what qualifies as great call center customer service?
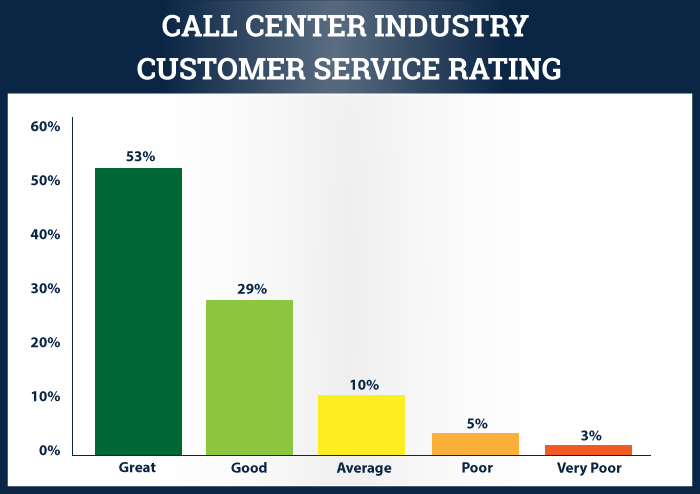
SQM research shows that the benchmark average for customer service for the "greatness rating" (top box response) in the call center industry is 53%. Of the over 500 call centers' SQM benchmarks annually, only 5% of them achieved our world-class customer service standard of 65% or higher greatness (top box response) rating average. Therefore, great call center customer service can be defined as the world-class standard of 65% or higher top box great rating response.
Moreover, most call centers' SQM measures for customer service would be classified as good performers. Therefore, you could argue that good customer service is also the enemy of the call center industry because they are not motivated to be great at service delivery. Furthermore, SQM research shows that the greatness rating on average drops by 14% top box response for each additional call made to a call center trying to resolve an inquiry or problem.
It's highly unlikely you can deliver great call center CX if you don't measure CX and can't measure without customer feedback information. Put differently, without customer feedback; you will be unsuccessful in providing excellent CX.
By asking customers for feedback about their call center interaction, you can get valuable insight for assessing and improving CX. Below are the main reasons why collecting customer feedback about their call center experience is important:
- CX benchmarking for understanding how your call center and agent compares
- Relationship builder shows your listening and cares about delivering great CX
- Performance indicator for learning about what customers like and don't like
- Alert system to provide service recovery and retention
- Referral advocates are generated based on positive customer feedback
- Ideal generator to discover the opportunities for improving CX and profits
- Agent feedback for assessing their CX performance and providing coaching
- CX recognition is a powerful business practice for motivating agents

What Is a Customer Feedback Loop?
A customer feedback loop is a CX strategy to continuously improve the call resolution of customer interactions on the first call and deliver great Csat. The customer feedback loop journey is circular, representing a continuous improvement process for improving the customer journey using a call center. The customer feedback loop can be used at the call center or the agent level.
Call center leaders are increasing investments in customer service QA software that employs a customer feedback loop process. At SQM, our QA customer feedback loop process consists of four steps – Identify, Develop, Check, and Act (IDCA) to improve FCR, Csat, and customer service performance. The customer feedback loop feature is available on our mySQM™ customer service QA software. The four ongoing sequential steps of our customer feedback loop IDCA process are:
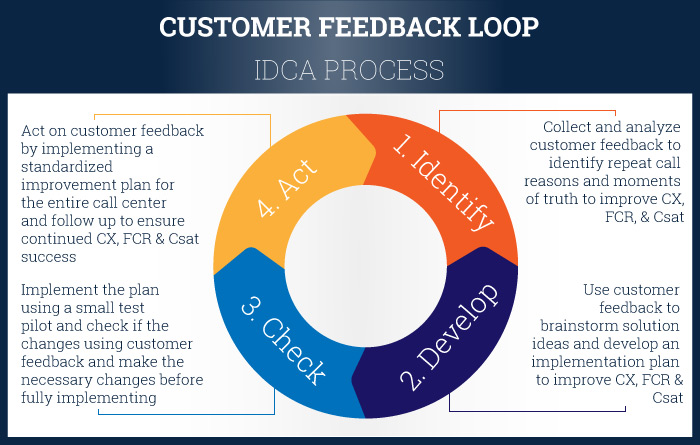
1. Identify Opportunities to Improve CX
The objective for the first stage is to identify and analyze repeat call reasons and moments of truth (MoT) that need to be improved to increase FCR, Csat, and lower operating costs. Next, customer feedback is used to assess CX's performance and identify opportunities to enhance and design people, processes, and technology practices needed to meet customer needs.
The eight customer feedback collection methods below can be used to analyze and understand how to take action to improve CX. Therefore, the customer feedback approach for improving call center operations can be described as an Outside-in CX operating practice.
The Outside-In CX operating practice requires the call center to be customer-centric. Therefore, call centers using this approach incorporate customer feedback into all aspects of their operating practices.
With the Outside-In CX operating practice, the customer defines CX. With the Inside-Out CX operating practice, the organization defines CX. Arguably, the Outside-In CX operating practice is the better of the two CX operating practices.
Customers often point out pain points and opportunities to improve CX that employees working inside the organization can overlook due to the Inside-out CX operating practice perspective.
After gathering the appropriate amount of customer feedback, you need to analyze it to determine the opportunities to improve CX. This is done using a repeat call reason tally report or the CX journey map. After identifying opportunities to improve CX, select top repeat call reasons to improve by using a selection grid (criteria = doable, FCR & Csat gains, cost, and risk) to determine what repeat call reasons should be improved.
2. Develop an Action Plan to Improve CX
After determining the repeat call reasons and MoT that need to be improved, you are ready for the second stage of the customer feedback loop for developing an action plan to improve CX (e.g., FCR and Csat). The specific objective of this stage is to create and present solutions for improving CX.
Specifically, you need to generate and select solution ideas in this stage. This is done by brainstorming solution ideas and using a selection grid (criteria = doable, FCR & Csat gains, cost, and risk) to determine what solution should be used and present these ideas to the senior management team.
The final step in this stage is developing an action plan to improve CX. The action plan should include when, how, for whom, what solution ideas will be implemented, and success criteria. After completing the plan, present the action plan for implementing CX improvements. However, before presenting to the senior management team, it is helpful to gain the necessary support for the action plan.
3. Check to See if CX has Improved
The third stage is about checking to see if CX has improved. The specific objective is to implement and see if the action plan has improved CX for reducing repeat calls or enhancing CX. Typically CX improvement success criteria are improving FCR, Csat, customer referral, and retention.
The check stage is about implementing the action plan and evaluating CX improvement. This is done by implementing the action plan on a small scale to determine the impact of the change. Again, the success criteria for checking the results of the test pilot should be based on VoC performance.
If possible, check one solution idea at a time. In this stage, it may be necessary to make changes to improve CX. If the success criteria are achieved, proceed to full implementation. If the CX success criteria are not fulfilled, review implementation execution or develop a revised plan. Do not proceed to stage four until you have achieved the CX success criteria.
4. Act on Customer Feeback
The fourth stage is to act on customer feedback by implementing a standardized improvement plan for the entire call center and follow up to ensure continued CX, FCR & Csat success.
The specific objective is to achieve the most significant benefit from improving CX by reducing repeat contacts and enhancing MoT. In this stage, call centers standardize solution ideas for operating procedure changes.
This is done by developing a 'solution idea operating procedure changes' manual to ensure a standardized execution. A well-documented standardized operating procedure captured and stored in a knowledge management tool is critical for ensuring proper implementation of the solution ideas within the entire contact center.
In this stage, it is necessary to monitor solution idea changes. Again, this is done using customer feedback and CX criteria to determine if the solution ideas have been adequately implemented. Once the solution ideas have been fully implemented, continue to look for incremental improvements to refine the solution. Again, it is essential to share CX results with employees and customers.
How to Collect Customer Feedback?
Below are the eight best ways to collect customer feedback for call centers. The customer feedback methods are not ranked for importance. However, it is common for top-performing call centers for customer service delivery to use all eight best ways to collect customer feedback.
Post-Contact Survey (e.g., phone, email & online)
A post-contact survey is conducted after a customer interaction using a touchpoint (e.g., call center, email, IVR, chat, and website) to capture customer feedback. Post-contact surveys are triggered (within one day) after using a touchpoint. For example, once an interaction ends, a customer is invited to complete a post-call phone, email, or online survey to determine if their interaction was resolved on the first call, satisfaction, and opportunities to improve CX.
Call centers use a post-call survey to gather customer feedback, analyze the collected data to assess CX performance, and report it to help improve their service delivery. Furthermore, using post-call survey data and feedback is a best practice for determining agent Csat delivery and coaching them to provide great customer service.
Post-call surveying methods remain popular for assessing CX performance and opportunities for improving CX. However, they are viewed as one of the most costly methods for collecting customer feedback, and customer fatigue can be an issue.
Furthermore, many call centers still use post-call survey data and feedback for agent coaching and accountability. In addition, post-call surveys are used to ask callers specific questions about their interaction with the call center experience and provide the following CX insights:
- First Call Resolution
- Customer Satisfaction
- Call Center CX Greatness
- Agent's Ability to Resolve Calls
- Interactional NPS
- Root Causes for non-FCR
- Repeat Call Reasons
- Opportunities to Improve CX
Agent Ask Customer
An agent asking the customer about their experience entails them using a call resolution question at the end of a call. The two typical call resolution options are, "Did I resolve the reason for your call today?" or "Did I give you clear next steps to resolve your call?"
In many cases, call centers set a target that the agent asks the customer on 90% of their calls, "Did I resolve the reason for your call today?" and for 10% of their calls, the agent asks, "Did I give you clear next steps to resolve your call?" Some agents are uncomfortable asking customers these questions.
Many call centers use speech analytics or QA monitoring to measure if the agent asked the customer a call resolution question. This method can inflate FCR and call resolution because the customer can be reluctant to be candid about answering the call resolution question to the agent they are speaking to about their call reason. However, this method can help motivate an agent to go the extra mile to resolve a customer's call.
Speech Analytics
Speech analytics uses audio recordings and analyzes that data to transcribe for relevant and meaningful customer experience intelligence. Put simply, speech analytics software takes customer recordings and transcribes them into text for analysis.
Speech analytics helps call centers assess their agent's quality assurance by evaluating all or most calls and automatically scoring calls for compliance and CX performance. Furthermore, speech analytics can help identify CX improvement opportunities and service recovery.
Your quality assurance (QA) can be improved using the insights you glean from speech analytics, and agents will have a less biased QA score for their performance. However, speech analytics is not a substitute for post-call surveying because it does not capture the customer satisfaction of their experience as effectively as a customer survey.
Social Media & Review Sites
Your customers often share their experience using your call center, products, and services via social media and review sites. As a result, most companies understand the importance of acquiring online customer reviews for their business to help them with revenue growth. According to a HubSpot Research survey, 1/3 of respondents said review sites played an essential role in their purchasing decision-making process.
For social media and review sites, negative or positive customer feedback provide a call center with an opportunity to improve CX and provide service recovery. In addition, customer feedback allows employees insights into where your call center and the company are failing to meet customer needs and can help remove common roadblocks in the customer journey.
Customer Quality Assurance
Many call centers include the call resolution metric in their QA form and practices to determine call resolution performance. This method can help motivate an agent to go the extra mile to resolve a customer's call. However, this method can inflate call resolution performance. SQM has found that QA evaluators tend to be easier graders than customers when determining if the call is resolved.
However, a best practice is to include call resolution and Csat survey results in what SQM calls a customer quality assurance form. This approach makes the QA process much more impactful for improving service and cost because it utilizes customer feedback. For example, customer quality assurance combines call compliance metrics, judged by a QA evaluator, and service quality metrics, judged by a customer via a post-call or email customer survey for assessing the same call.
Based on conducting hundreds of QA case studies with leading North American call centers, SQM's research shows that a whopping 81% of agents' had no Csat, FCR, or call resolution improvement resulting from traditional QA evaluations. The low correlation between traditional QA and FCR ratings is because the customer is not the judge of whether FCR or call resolution took place. Conversely, over 70% of call centers improve FCR and Csat using the CQA approach.
Operational Data
Operational data is available via ACD, case management, assisted calls, and CRM software and are used to analyze whether the customer's call was resolved on the first call and CX. One of the main advantages of using an ACD, case management, or CRM system is that the call center can measure FCR and manage CX using big data (e.g., all calls).
Furthermore, most call centers already have operational data from ACD, case management, assisted calls, and CRM sources, so it is a low-cost FCR and CX measurement method. However, it is common for case management and CRM that the agent determines if the call is resolved or the case is closed, and as a result, this internal method can be prone to agent manipulation. Similar to other internal FCR measurement methods (e.g., ACD), case management and CRM methods can substantially overstate FCR.
Although, utilizing operational data can provide tremendous insights for improving CX. For example, calls that require agents to ask for help from helpdesk agents can be tagged for identifying areas where agents need more coaching and training to improve their CX performance.

Quick Related Links
First Call Resolution Comprehensive Guide Customer Satisfaction Comprehensive Guide Top 10 CX Questions Top 10 CX Metrics VoC Closed-loop Good to Great Customer Service

